How to create Alignment between OKRs
View your Alignment Map.
Read more about aligning Company and Team OKRs in this Knowledge Base article.
What is Alignment?
Alignment is the hierarchical linking of Objectives to show how they contribute to each other. It is a powerful way to visualise how the work being done at all levels of your organisation connects to the top level strategic goals.
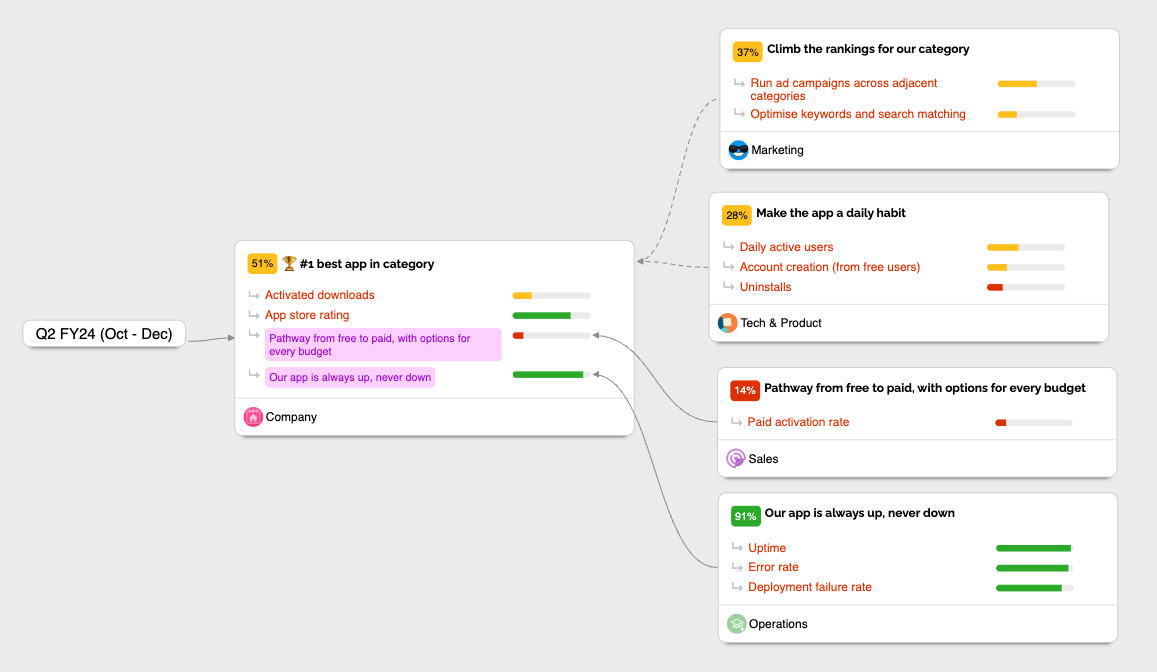
In OKR Dash, Objectives can be aligned to a single parent Objective when they are created or edited. This creates a tree structure of Objectives that can be explored in the Tree view (also called the Alignment Map view).
When a Key Result is updated, its progress can optionally contribute to the progress of its parent Objective, and this contribution can cascade up through multiple levels of aligned Objectives. This allows high level Objectives to reflect the progress of the work being done at lower levels.
Managing alignment between Objectives
There are two ways to do this:
Firstly, when editing the OKR:
When creating or editing an Objective, you can choose a parent Objective from the dropdown. This will create an alignment between the two Objectives, optionally contributing progress.
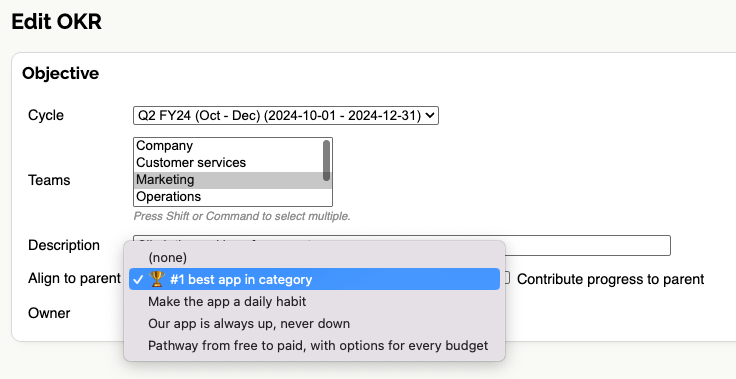
Only Objectives within the same Cycle can be aligned together. If you need to align Objectives across different Cycles, consider duplicating the Objective into the relevant Cycle.
To remove an alignment, simply edit the Objective and set the parent Objective to "None".
Secondly, from the Tree view:
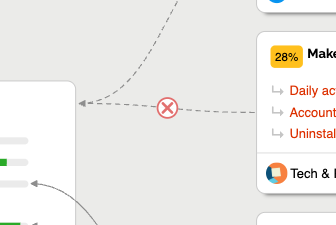
Here the hierarchical structure is visualised. You can click on a relationship to delete it:
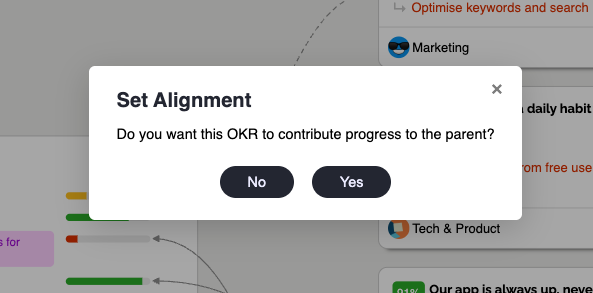
Or you can drag and drop arrows between Objectives to create new alignments, which can optionally contribute progress to the parent:
Watch a video of this in action.
When a contributing alignment is created or deleted, a special lightweight Key Result is added to the parent to represent the relationship, and the progress of the parent Objective will be recalculated immediately to reflect the change.